Browse All Articles > Resetting the Exchange 2000/2003 Log Sequence
Unlike Exchange 2007, which supports a logs sequence of 2,000,000,000, the largest transaction log number for Exchange 2000 and 2003 is FFFF0. That number in decimal is 1,048,560. (Which is the maximum number of log files that can be written sequentially).
While it can take a very very long time for this to happen, I have had to do it a few times over the years. When the transaction log sequence is reached, the Microsoft Jet database engine returns error -519, IS error and the stores dismount.
You will see the following in the event viewer when the sequence is getting close to being exhausted.
--
Event ID 514:
Source: ESE
Category: Logging/Recovery
Information Store (7468) Exchange Users: Log sequence numbers for this instance have almost been completely consumed. The current log generation is 932000 (0x000E38A0) which is approaching the maximum log generation of 1048559 (0x000FFFEF), there are 116559 (0x0001C74F) log generations left to be used. To begin renumbering from generation 1, the instance must be shutdown cleanly and all log files must be deleted. Backups will be invalidated.
--
The intent of this article is to outline the steps to be followed for resetting the Exchange log sequence for a particular server\storage group. There are two ways to reset the log sequence. The first is automatic and utilizes the Exchange Database Recovery Management tool (Requires an Exchange 2007 server). The second is a more manual process but works just the same. The article will cover both methods.
1. Verify that no backups are running on the Exchange server. Stores will not dismount if a backup is in progress.
2. Note the log file naming convention for the particular storage group you are working with. Right-click the storage group and select properties.
![Verify SG Logs Naming Prefix]()
3. From ESM (Exchange System Manager), dismount all the stores within the storage group
![Dismount Stores]()
4. Open a CMD prompt and use Eseutil to verify stores are in a “Clean Shutdown” state
eseutil /mh f:\db1\sg1_db1.edb (needs to be run against each store)
![Verify Store Shutdown State]()
If the database has not been correctly detached, the state value is “Dirty Shutdown” or “Inconsistent”. This means that some of the existing transaction log files contain outstanding transactions that are required by the database. If you remove the transaction log files in this situation, the database cannot be started again unless you restore the database from a backup or unless you repair the database by using the Eseutil command and the Isinteg command.
Automatic Method
The automatic method requires the Exchange Database Recovery Management Tool. The tool is run from an Exchange 2007 server and can be used to connect to your 2000/2003 server.
1. Click on the Database Recovery Management link from the Exchange 2007 Management Console (Under Toolbox)
![Database Recovery Management Link]()
2. Enter Exchange and Domain Controller information
![Enter Exchange and Domain Controller information]()
3. Choose the "Reset log generation number" task
![Reset log generation number task]()
4. Select a backup location for the logs
![Select backup location for the logs]()
5. Confirm options
![Confirm options]()
6. The reset log generation process begins
![The reset log generation process begins]()
7. Once the process is complete, you will see a completion successful screen which shows each log that was moved
![reset log generation process successful]()
8. Check logs directory and verify log sequence has been reset
![Verify log sequence]()
Manual Method
In the event you do not have access to the Database Recovery Management tool, you must move and then delete the logs and checkpoint files manually. Like the automatic method, you will need to verify backups are not running, dismount the stores and verify stores are in a clean shutdown state before proceeding.
1. Copy logs and checkpoint file (all files) from Logs drive to alternate location
![Copy logs and checkpoint file (]()
2. Delete logs and checkpoint file from Logs drive
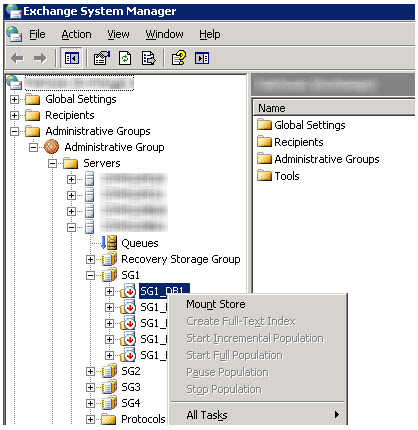
3. Mount stores
![Mount stores]()
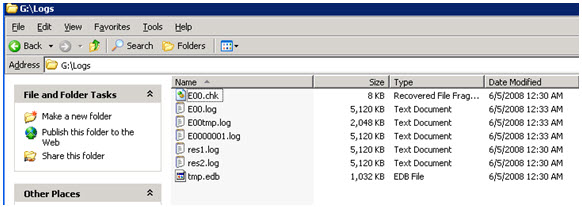
4. Verify the log sequence has been reset
![Verify log sequence2]()
Done!
--
More info regarding the Exchange log sequence and the tools used can be found here:
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/830408
http://msexchangeteam.com/archive/2004/05/12/130556.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa998611(EXCHG.80).aspx
While it can take a very very long time for this to happen, I have had to do it a few times over the years. When the transaction log sequence is reached, the Microsoft Jet database engine returns error -519, IS error and the stores dismount.
You will see the following in the event viewer when the sequence is getting close to being exhausted.
--
Event ID 514:
Source: ESE
Category: Logging/Recovery
Information Store (7468) Exchange Users: Log sequence numbers for this instance have almost been completely consumed. The current log generation is 932000 (0x000E38A0) which is approaching the maximum log generation of 1048559 (0x000FFFEF), there are 116559 (0x0001C74F) log generations left to be used. To begin renumbering from generation 1, the instance must be shutdown cleanly and all log files must be deleted. Backups will be invalidated.
--
The intent of this article is to outline the steps to be followed for resetting the Exchange log sequence for a particular server\storage group. There are two ways to reset the log sequence. The first is automatic and utilizes the Exchange Database Recovery Management tool (Requires an Exchange 2007 server). The second is a more manual process but works just the same. The article will cover both methods.
1. Verify that no backups are running on the Exchange server. Stores will not dismount if a backup is in progress.
2. Note the log file naming convention for the particular storage group you are working with. Right-click the storage group and select properties.

3. From ESM (Exchange System Manager), dismount all the stores within the storage group
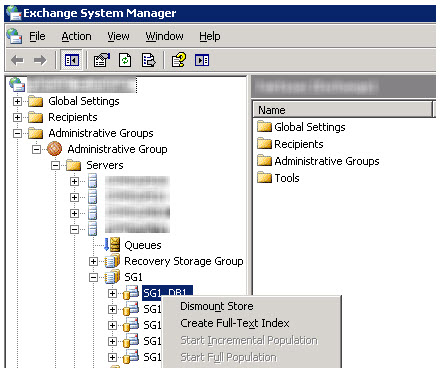
4. Open a CMD prompt and use Eseutil to verify stores are in a “Clean Shutdown” state
eseutil /mh f:\db1\sg1_db1.edb (needs to be run against each store)
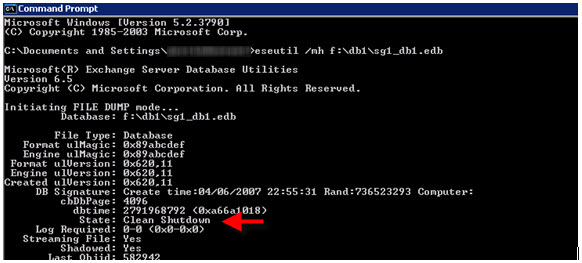
If the database has not been correctly detached, the state value is “Dirty Shutdown” or “Inconsistent”. This means that some of the existing transaction log files contain outstanding transactions that are required by the database. If you remove the transaction log files in this situation, the database cannot be started again unless you restore the database from a backup or unless you repair the database by using the Eseutil command and the Isinteg command.
Automatic Method
The automatic method requires the Exchange Database Recovery Management Tool. The tool is run from an Exchange 2007 server and can be used to connect to your 2000/2003 server.
1. Click on the Database Recovery Management link from the Exchange 2007 Management Console (Under Toolbox)

2. Enter Exchange and Domain Controller information

3. Choose the "Reset log generation number" task
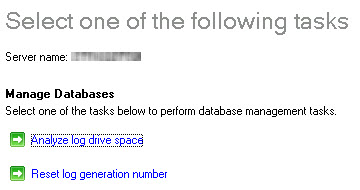
4. Select a backup location for the logs

5. Confirm options

6. The reset log generation process begins

7. Once the process is complete, you will see a completion successful screen which shows each log that was moved

8. Check logs directory and verify log sequence has been reset
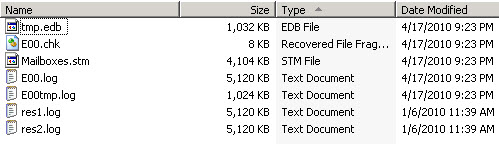
Manual Method
In the event you do not have access to the Database Recovery Management tool, you must move and then delete the logs and checkpoint files manually. Like the automatic method, you will need to verify backups are not running, dismount the stores and verify stores are in a clean shutdown state before proceeding.
1. Copy logs and checkpoint file (all files) from Logs drive to alternate location
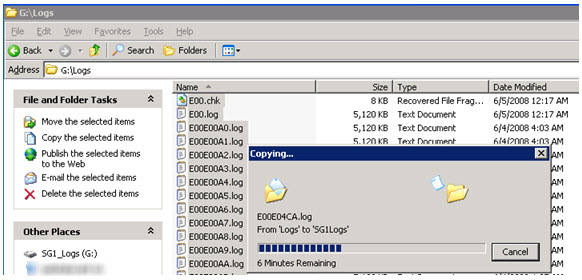
2. Delete logs and checkpoint file from Logs drive
3. Mount stores
4. Verify the log sequence has been reset
Done!
--
More info regarding the Exchange log sequence and the tools used can be found here:
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/830408
http://msexchangeteam.com/archive/2004/05/12/130556.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa998611(EXCHG.80).aspx
Have a question about something in this article? You can receive help directly from the article author. Sign up for a free trial to get started.


Comments (8)
Commented:
Author
Commented:Commented:
Author
Commented:Commented:
View More