How to use product version as a constant
Ok, here is my problem. I want to show the assembly version (product version) on an about form. Currently I am doing so by using the Application Class and the ProductVersion property. Everything works fine UNTIL I protect the assembly with an obfuscation system. When I do so the ProductVersion property always returns 1.0.0.0
I know the obfuscation system well and there is no way to resolve this without sacrificing some of the strong protection it provides. I have even strong named the assembly but get the same result. So here is my proposed solution, though I don't know how to implement it, or if it is even possible.
Is there any way to assign the product version to a constant during compilation?
Proposed example:
private const string MyProductVersion = some kind of replaceable parameter during compilation.
This way it would be hard coded (which is fine) and would solve the problem since this is the way I wound up having to do it by hand. I use an auto-incrementing version system so every time I release an update I have to manually check the assembly info and put it into the source code constant. If I forget a previous version number is displayed and creates havoc.
Thanks in advance
I know the obfuscation system well and there is no way to resolve this without sacrificing some of the strong protection it provides. I have even strong named the assembly but get the same result. So here is my proposed solution, though I don't know how to implement it, or if it is even possible.
Is there any way to assign the product version to a constant during compilation?
Proposed example:
private const string MyProductVersion = some kind of replaceable parameter during compilation.
This way it would be hard coded (which is fine) and would solve the problem since this is the way I wound up having to do it by hand. I use an auto-incrementing version system so every time I release an update I have to manually check the assembly info and put it into the source code constant. If I forget a previous version number is displayed and creates havoc.
Thanks in advance
ASKER
Yes, the problem is after obfuscation the version number is not able to be read properly.
*No Points*
Just to add to what Fernando has stated, you can also add a level of *granularity* by getting the build, major, minor and revision.
Some additional methods:
-saige-
Just to add to what Fernando has stated, you can also add a level of *granularity* by getting the build, major, minor and revision.
Some additional methods:
/// <summary>Class used to gather executable and dynamic link library information.</summary>
public sealed class Executables
{
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Build Version.</summary>
public static string AssemblyBuildVersion
{
get { return Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetName().Version.Build.ToString(); }
}
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Copyright information.</summary>
public static string AssemblyCopyright
{
get
{
object[] attributes = Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetCustomAttributes(typeof(AssemblyCopyrightAttribute), false);
return (attributes != null && attributes.Length > 0) && ((AssemblyCopyrightAttribute)attributes[0] != null) ? ((AssemblyCopyrightAttribute)attributes[0]).Copyright : string.Empty;
}
}
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Guid.</summary>
public static string AssemblyGuid
{
get
{
object[] attributes = Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetCustomAttributes(typeof(GuidAttribute), false);
return attributes != null && attributes.Length > 0 ? ((GuidAttribute)attributes[0]).Value : string.Empty;
}
}
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Major Version.</summary>
public static string AssemblyMajorVersion
{
get { return Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetName().Version.Major.ToString(); }
}
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Minor Version.</summary>
public static string AssemblyMinorVersion
{
get { return Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetName().Version.Minor.ToString(); }
}
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Revision Version.</summary>
public static string AssemblyRevisionVersion
{
get { return Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetName().Version.Revision.ToString(); }
}
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Title.</summary>
public static string AssemblyTitle
{
get
{
object[] attributes = Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetCustomAttributes(typeof(AssemblyTitleAttribute), false);
return (attributes != null && attributes.Length > 0) && (((AssemblyTitleAttribute)attributes[0]).Title != "") ? ((AssemblyTitleAttribute)attributes[0]).Title : Path.GetFileNameWithoutExtension(Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().CodeBase);
}
}
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Version.</summary>
public static string AssemblyVersion
{
get
{
object[] attributes = Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetCustomAttributes(typeof(AssemblyVersionAttribute), false);
return attributes != null && attributes.Length > 0 ? ((AssemblyVersionAttribute)attributes[0]).Version : string.Empty;
}
}
}-saige-
So exptech, you are stating the the obfuscation is even modifying the assembly metadata? Interesting. Which obfuscater are you using?
-saige-
-saige-
ASKER
Please read my comment above. I appreciate the answers but they won't solve my problem.
ASKER
Dot net Reactor. Yes, in fact it even resigns the assembly.
ASKER
Actually, sometimes it does show the correct version number, but most of the time it does not. I am in touch with the company on the issue but in the meantime I need another solution.
According to their site, you can use the ObfuscationAttribute class.
-saige-
.NET Reactor automatically detects the attribute and excludes the corresponding types and members from obfuscation.Example code posted from MSDN:
using System;
using System.Reflection;
// Mark this public assembly for obfuscation.
[assembly:ObfuscateAssemblyAttribute(false)]
// This class is marked for obfuscation, because the assembly
// is marked.
public class Type1
{
// Exclude this method from obfuscation. The default value
// of the Exclude property is true, so it is not necessary
// to specify Exclude=True, although spelling it out makes
// your intent clearer.
[ObfuscationAttribute(Exclude=true)]
public void MethodA() {}
// This member is marked for obfuscation because the class
// is marked.
public void MethodB() {}
}
// Exclude this type from obfuscation, but do not apply that
// exclusion to members. The default value of the Exclude
// property is true, so it is not necessary to specify
// Exclude=true, although spelling it out makes your intent
// clearer.
[ObfuscationAttribute(Exclude=true, ApplyToMembers=false)]
public class Type2
{
// The exclusion of the type is not applied to its members,
// however in order to mark the member with the "default"
// feature it is necessary to specify Exclude=false,
// because the default value of Exclude is true. The tool
// should not strip this attribute after obfuscation.
[ObfuscationAttribute(Exclude=false, Feature="default",
StripAfterObfuscation=false)]
public void MethodA() {}
// This member is marked for obfuscation, because the
// exclusion of the type is not applied to its members.
public void MethodB() {}
}
// This class only exists to provide an entry point for the
// assembly and to display the attribute values.
internal class Test
{
public static void Main()
{
// Display the ObfuscateAssemblyAttribute properties
// for the assembly.
Assembly assem = typeof(Test).Assembly;
object[] assemAttrs = assem.GetCustomAttributes(
typeof(ObfuscateAssemblyAttribute), false);
foreach( Attribute a in assemAttrs )
{
ShowObfuscateAssembly((ObfuscateAssemblyAttribute) a);
}
// Display the ObfuscationAttribute properties for each
// type that is visible to users of the assembly.
foreach( Type t in assem.GetTypes() )
{
if (t.IsVisible)
{
object[] tAttrs = t.GetCustomAttributes(
typeof(ObfuscationAttribute), false);
foreach( Attribute a in tAttrs )
{
ShowObfuscation(((ObfuscationAttribute) a),
t.Name);
}
// Display the ObfuscationAttribute properties
// for each member in the type.
foreach( MemberInfo m in t.GetMembers() )
{
object[] mAttrs = m.GetCustomAttributes(
typeof(ObfuscationAttribute), false);
foreach( Attribute a in mAttrs )
{
ShowObfuscation(((ObfuscationAttribute) a),
t.Name + "." + m.Name);
}
}
}
}
}
private static void ShowObfuscateAssembly(
ObfuscateAssemblyAttribute ob)
{
Console.WriteLine("\r\nObfuscateAssemblyAttribute properties:");
Console.WriteLine(" AssemblyIsPrivate: {0}",
ob.AssemblyIsPrivate);
Console.WriteLine(" StripAfterObfuscation: {0}",
ob.StripAfterObfuscation);
}
private static void ShowObfuscation(
ObfuscationAttribute ob, string target)
{
Console.WriteLine("\r\nObfuscationAttribute properties for: {0}",
target);
Console.WriteLine(" Exclude: {0}", ob.Exclude);
Console.WriteLine(" Feature: {0}", ob.Feature);
Console.WriteLine(" StripAfterObfuscation: {0}",
ob.StripAfterObfuscation);
Console.WriteLine(" ApplyToMembers: {0}", ob.ApplyToMembers);
}
}
/* This code example produces the following output:
ObfuscateAssemblyAttribute properties:
AssemblyIsPrivate: False
StripAfterObfuscation: True
ObfuscationAttribute properties for: Type1.MethodA
Exclude: True
Feature: all
StripAfterObfuscation: True
ApplyToMembers: True
ObfuscationAttribute properties for: Type2
Exclude: True
Feature: all
StripAfterObfuscation: True
ApplyToMembers: False
ObfuscationAttribute properties for: Type2.MethodA
Exclude: False
Feature: default
StripAfterObfuscation: False
ApplyToMembers: True
*/-saige-
ASKER
it_saige,
I was not aware of that class but I am not sure how I would use it. The problem is not the code that reads and displays the Application.ProductVersion
I was not aware of that class but I am not sure how I would use it. The problem is not the code that reads and displays the Application.ProductVersion
I would first try excluding the method that returns the AssemblyVersion (espcially if it is a part of the Assembly, this is where the obfuscation is probably occuring); i.e. - (Using my implementation above it would look something like):
If this does not bear any fruit then creating a property as you were thinking should do the trick:
-saige-
/// <summary>Class used to gather executable and dynamic link library information.</summary>
[ObfuscationAttribute(Exclude = true, ApplyToMembers = true)]
public sealed class Executables
{
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Build Version.</summary>
public static string AssemblyBuildVersion
{
get { return Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetName().Version.Build.ToString(); }
}
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Copyright information.</summary>
public static string AssemblyCopyright
{
get
{
object[] attributes = Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetCustomAttributes(typeof(AssemblyCopyrightAttribute), false);
return (attributes != null && attributes.Length > 0) && ((AssemblyCopyrightAttribute)attributes[0] != null) ? ((AssemblyCopyrightAttribute)attributes[0]).Copyright : string.Empty;
}
}
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Guid.</summary>
public static string AssemblyGuid
{
get
{
object[] attributes = Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetCustomAttributes(typeof(GuidAttribute), false);
return attributes != null && attributes.Length > 0 ? ((GuidAttribute)attributes[0]).Value : string.Empty;
}
}
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Major Version.</summary>
public static string AssemblyMajorVersion
{
get { return Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetName().Version.Major.ToString(); }
}
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Minor Version.</summary>
public static string AssemblyMinorVersion
{
get { return Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetName().Version.Minor.ToString(); }
}
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Revision Version.</summary>
public static string AssemblyRevisionVersion
{
get { return Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetName().Version.Revision.ToString(); }
}
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Title.</summary>
public static string AssemblyTitle
{
get
{
object[] attributes = Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetCustomAttributes(typeof(AssemblyTitleAttribute), false);
return (attributes != null && attributes.Length > 0) && (((AssemblyTitleAttribute)attributes[0]).Title != "") ? ((AssemblyTitleAttribute)attributes[0]).Title : Path.GetFileNameWithoutExtension(Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().CodeBase);
}
}
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Version.</summary>
public static string AssemblyVersion
{
get
{
object[] attributes = Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetCustomAttributes(typeof(AssemblyVersionAttribute), false);
return attributes != null && attributes.Length > 0 ? ((AssemblyVersionAttribute)attributes[0]).Version : string.Empty;
}
}
}If this does not bear any fruit then creating a property as you were thinking should do the trick:
public static Globals
{
private readonly static string fMyVersion = "1.0.0.0";
[ObfuscationAttribute(Exclude = true)]
public static string MyVersion { get { return fMyVersion; } }
}-saige-
ASKER
I am going to try this now.
ASKER
OK, now this is really crazy. When I use the following line of code you suggested:
get { return Assembly.GetEntryAssembly(
and I protect the application it will not even run. It just starts and stops.
If I replace it with:
get { return Application.ProductVersion
then it runs fine but returns the wrong version #.
For some reason it runs when I use the Application class but not the Assembly class.
Your last idea:
public static Globals
{
private readonly static string fMyVersion = "1.0.0.0";
[ObfuscationAttribute(Excl
public static string MyVersion { get { return fMyVersion; } }
}
is what I am doing now, but is there any way to have the version number automatically assigned to the fMyVersion field during complitation? I could make fMyVersion a constant but I don't know of any way to assign a value to a constant when compiling.
get { return Assembly.GetEntryAssembly(
and I protect the application it will not even run. It just starts and stops.
If I replace it with:
get { return Application.ProductVersion
then it runs fine but returns the wrong version #.
For some reason it runs when I use the Application class but not the Assembly class.
Your last idea:
public static Globals
{
private readonly static string fMyVersion = "1.0.0.0";
[ObfuscationAttribute(Excl
public static string MyVersion { get { return fMyVersion; } }
}
is what I am doing now, but is there any way to have the version number automatically assigned to the fMyVersion field during complitation? I could make fMyVersion a constant but I don't know of any way to assign a value to a constant when compiling.
That particular method returns the build portion of the version. For the AssemblyVersion you would use:
My question would be where is it failing at, if you debug it do you get an exception. You could always include a try catch around the return.
As for the constant. If your code is not able to provide you with the version as assigned in the AssemblyInfo.cs, then trying to use a method to return the value to the fMyVersion backing field will result in the same obfuscation.
Matter of fact, now you are making me wonder why the build version caused a failure. I'm going to build a quick test project (unfortunately I do not have .Net Reactor, I wonder if they have a 30-day trial. ;) )
-saige-
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Version.</summary>
public static string AssemblyVersion
{
get
{
object[] attributes = Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetCustomAttributes(typeof(AssemblyVersionAttribute), false);
return attributes != null && attributes.Length > 0 ? ((AssemblyVersionAttribute)attributes[0]).Version : string.Empty;
}
}My question would be where is it failing at, if you debug it do you get an exception. You could always include a try catch around the return.
As for the constant. If your code is not able to provide you with the version as assigned in the AssemblyInfo.cs, then trying to use a method to return the value to the fMyVersion backing field will result in the same obfuscation.
Matter of fact, now you are making me wonder why the build version caused a failure. I'm going to build a quick test project (unfortunately I do not have .Net Reactor, I wonder if they have a 30-day trial. ;) )
-saige-
Ok. Had to make a change to the AssemblyVersion method. But it all works fine for me:
Unprotected output -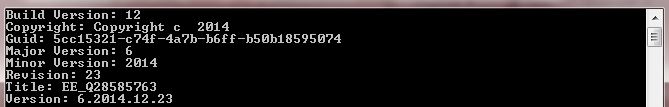
Protected output -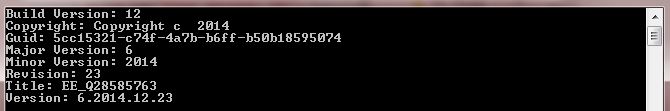
-saige-
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace EE_Q28585763
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Build Version: {0}", Executables.AssemblyBuildVersion);
Console.WriteLine("Copyright: {0}", Executables.AssemblyCopyright);
Console.WriteLine("Guid: {0}", Executables.AssemblyGuid);
Console.WriteLine("Major Version: {0}", Executables.AssemblyMajorVersion);
Console.WriteLine("Minor Version: {0}", Executables.AssemblyMinorVersion);
Console.WriteLine("Revision: {0}", Executables.AssemblyRevisionVersion);
Console.WriteLine("Title: {0}", Executables.AssemblyTitle);
Console.WriteLine("Version: {0}", Executables.AssemblyVersion);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
/// <summary>Class used to gather executable and dynamic link library information.</summary>
[ObfuscationAttribute(Exclude = true, ApplyToMembers = true)]
public sealed class Executables
{
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Build Version.</summary>
public static string AssemblyBuildVersion
{
get { return Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetName().Version.Build.ToString(); }
}
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Copyright information.</summary>
public static string AssemblyCopyright
{
get
{
object[] attributes = Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetCustomAttributes(typeof(AssemblyCopyrightAttribute), false);
return (attributes != null && attributes.Length > 0) && ((AssemblyCopyrightAttribute)attributes[0] != null) ? ((AssemblyCopyrightAttribute)attributes[0]).Copyright : string.Empty;
}
}
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Guid.</summary>
public static string AssemblyGuid
{
get
{
object[] attributes = Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetCustomAttributes(typeof(GuidAttribute), false);
return attributes != null && attributes.Length > 0 ? ((GuidAttribute)attributes[0]).Value : string.Empty;
}
}
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Major Version.</summary>
public static string AssemblyMajorVersion
{
get { return Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetName().Version.Major.ToString(); }
}
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Minor Version.</summary>
public static string AssemblyMinorVersion
{
get { return Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetName().Version.Minor.ToString(); }
}
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Revision Version.</summary>
public static string AssemblyRevisionVersion
{
get { return Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetName().Version.Revision.ToString(); }
}
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Title.</summary>
public static string AssemblyTitle
{
get
{
object[] attributes = Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetCustomAttributes(typeof(AssemblyTitleAttribute), false);
return (attributes != null && attributes.Length > 0) && (((AssemblyTitleAttribute)attributes[0]).Title != "") ? ((AssemblyTitleAttribute)attributes[0]).Title : Path.GetFileNameWithoutExtension(Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().CodeBase);
}
}
/// <summary>Gets the Assembly Version.</summary>
public static string AssemblyVersion
{
get
{
Version version = Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().GetName().Version;
return version != null && version.ToString().Length > 0 ? version.ToString() : string.Empty;
}
}
}
}Unprotected output -
Protected output -
-saige-
ASKER CERTIFIED SOLUTION
membership
This solution is only available to members.
To access this solution, you must be a member of Experts Exchange.
ASKER
It works. Thank you for the help !
Have you tried using the version number at runtime with code like this.
Open in new window