TMG Network integration
We have a corporate wide area network. The main site is using tmg 2010, and uses 192.168.0.0/22. Also we have two more site connected to the main site via a vpn tunnel provided by the ISP. The external sites are 172.16.32.0/24 and 172.16.64.0/24
Traffic between the nodes worked just fine until we implemented the tmg 2010 at the main site. We connect to the ISP via a public IP. Also the ISP provides the traffic coming from the other sites, but we have not been able yet to configure the tmg properly to allow the incoming traffic from those external sites.
Any suggestions?
Here is the network topology.
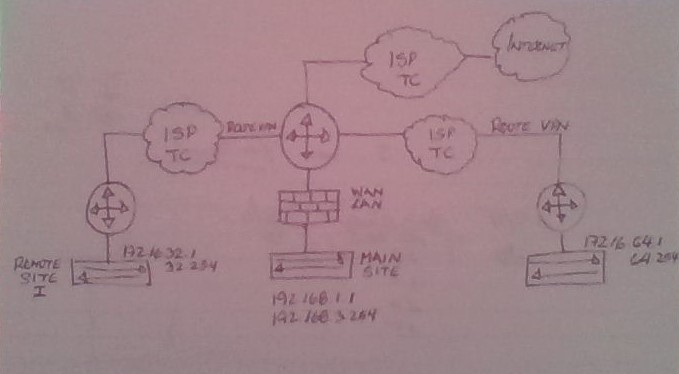
Traffic between the nodes worked just fine until we implemented the tmg 2010 at the main site. We connect to the ISP via a public IP. Also the ISP provides the traffic coming from the other sites, but we have not been able yet to configure the tmg properly to allow the incoming traffic from those external sites.
Any suggestions?
Here is the network topology.

This question needs an answer!
Become an EE member today
7 DAY FREE TRIALMembers can start a 7-Day Free trial then enjoy unlimited access to the platform.
View membership options
or
Learn why we charge membership fees
We get it - no one likes a content blocker. Take one extra minute and find out why we block content.
if I understand your picture in the right way, the VPN connection are handled by devices in front of TMG.
This means, that all other locations are transparently reachable via the routing rules of the routers.
And as it worked before, the routers do in general, what they should do...
From the TMG perspective, the TMG has to know, what to do with which targets and how to route them. Also you have to separate outgoing and incoming traffic and the traffic, which is targeted to the internet.
To tell TMG, that you have additional internal Networks (from the TMG perspective, a VPN endpoint is an internal target) you have to...
A.) Firewall-Polices - Toolbox - Network-Objects...
- Define a Address Range for any of your VPN remote locations...
- one for 172.16.32.0-172.16.32.255 (call it i.e. RemoteRange-01)
- one for 172.16.64.0-172.16.64.255 (call it i.e. RemoteRange-02)
B.) Networking - Network Rules
- Add routing rules (in front of the Internet Access Rule (the last one)...
- one Internal to Remote 1 - Relation Route - Source Internal - Destination RemoteRange-01
- one Internal to Remote 2 - Relation Route - Source Internal - Destination RemoteRange-02
C.) Networking - Networks
- following your picture, the routers, which creates the VPN tunnel are connected to the WAN interface...
- TMG handles all IP addresses on the WAN interface, which are not added to any other network.
- Means, your Internal Network contains only 192.168.x.x
- In this caser, nothing is to do... 172.16.x.x. is defined as external....
D.) Networking - Routing
- All traffic, which is not explicitly routed to any other target will follow the TMG default interface, which should be configured on the external interface. The TMG default gateway should point to the router, which handles the VPN tunnels and internet access.
- In your case, nothing to do here....
Now everything should work between the remote locations and the local network as it works between the Internet and the local network.
As there are always Firewall Policy Rules / Web Access Policies or Publishing rules between your internal network and your public network, you maybe limited by the rules which are already defined in TMG. You can not open everything to the remote networks while internet access is limited on the same logical interface.
You may check this with the live logging and what traffic is blocked and which not between your internal network and your remote locations.
(Logs & Reports --> logging -> Start a logging session between Source Network and Destination Network or better between two test clients (Client IP / Destination IP)
And here maybe starts the problem, as also your remote locations are defined as external by TMG... They come from the same interface than the internet traffic and TMG can not really separate what is really internet and what comes from the remote locations. .
It may be more logical from the TMG perspective, to create a separate network with its own adapter in a DMZ constellation. In this case, you TMG has 3 legs, one internal, one DMZ for the VPN connections and one really external to the internet. This way you can limit down the internet connection and open more widely the VPN remote networks. In this constellation, you need an additional network adapter with its own IP, a TMG network (Networking - Networks) where the new adapter is assigned too.. An network relation as Route and a routing rule which redirect the traffic to the IP address of the routing device on the DMZ leg. On this new leg, you connect a router which creates the VPN tunnel .
If you can take the same router depend a bit from the routing capabilities of this router.... If you can assign several IP addresses to the routers internal interface (the TMG side), you may NAT the traffic from the TMG public interface to the internet, and the traffic from the TMG DMZ interface via the VPN tunnels. Otherwise you need a dedicated VPN router, connected to the same ISP, with its own external IP address of course.
Another issue you should keep in mind is Routing and NAT.
The external interface of TMG is defined as NAT (by default).
Also your router may have a NAT relation to the internet, what would result into a double NAT.
Double NAT is always problematic, nevertheless is may work in most constellations.
The relation between your local network and the remote locations should be a pure routing relation. The VPN tunnel should be completely transparent.