IT
asked on
How to incorporate the codes from these questions already solved on experts exchange
How to incorporate the codes from these questions already solved on experts exchange for the text file I have attached. . Name of the text file is corpus.txt corpus.txt
This text file is a labelled data. It also contains unicode character, punctuation, html escape character, https, stop words.
Links to the question I am referring to are:
https://www.experts-exchange.com/questions/29096027/How-to-remove-unicode-characters-from-csv-file.html?anchorAnswerId=42543025#a42543025
https://www.experts-exchange.com/questions/29106263/replacing-hypertext-links-with-simple-text-'URL'.html?anchorAnswerId=42605405#a42605405
https://www.experts-exchange.com/questions/29106273/error-while-splitting-with-open-function-in-python.html?anchorAnswerId=42605423#a42605423
https://www.experts-exchange.com/questions/29106318/AttributeError-'list'-object-has-no-attribute-'split'-and-AttributeError-'numpy-ndarray'-object-has-no-attribute-'split'.html?anchorAnswerId=42606101#a42606101
All the accepted solutions for these links have been given by expert gelonida.
--------------------------
code to remove punctuation, to remove any number, or any stopword is:
--------------------------
import string
text = text.split()
re_punc = re.compile('[%s]' % re.escape(string.punctuati
text = [re_punc.sub('', w) for w in text]
text = [word for word in text if word.isalpha()]
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
stop_words = set(stopwords.words('engli
text = [w for w in text if not w in stop_words]
I want to store label column in d_y and text column in d_x. Then I want to apply cleaning in d_x which contains text.
with the help of accepted solution in above links, I am trying like this
--------------------------
import itertools
from itertools import islice
d = [ line.split('\t') for line in islice(open("corpus.txt"),
d_x = d[1]
d_y = d[0]
d_x # This does not give output as expected. It should contain the text from all rows
d_y # This does not give output as expected. It should contain all labels from all rows
--------------------------
My Intuition is to get a clean text file with label and text stored separately so that further modelling can be done on it.
This text file is a labelled data. It also contains unicode character, punctuation, html escape character, https, stop words.
Links to the question I am referring to are:
https://www.experts-exchange.com/questions/29096027/How-to-remove-unicode-characters-from-csv-file.html?anchorAnswerId=42543025#a42543025
https://www.experts-exchange.com/questions/29106263/replacing-hypertext-links-with-simple-text-'URL'.html?anchorAnswerId=42605405#a42605405
https://www.experts-exchange.com/questions/29106273/error-while-splitting-with-open-function-in-python.html?anchorAnswerId=42605423#a42605423
https://www.experts-exchange.com/questions/29106318/AttributeError-'list'-object-has-no-attribute-'split'-and-AttributeError-'numpy-ndarray'-object-has-no-attribute-'split'.html?anchorAnswerId=42606101#a42606101
All the accepted solutions for these links have been given by expert gelonida.
--------------------------
code to remove punctuation, to remove any number, or any stopword is:
--------------------------
import string
text = text.split()
re_punc = re.compile('[%s]' % re.escape(string.punctuati
text = [re_punc.sub('', w) for w in text]
text = [word for word in text if word.isalpha()]
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
stop_words = set(stopwords.words('engli
text = [w for w in text if not w in stop_words]
I want to store label column in d_y and text column in d_x. Then I want to apply cleaning in d_x which contains text.
with the help of accepted solution in above links, I am trying like this
--------------------------
import itertools
from itertools import islice
d = [ line.split('\t') for line in islice(open("corpus.txt"),
d_x = d[1]
d_y = d[0]
d_x # This does not give output as expected. It should contain the text from all rows
d_y # This does not give output as expected. It should contain all labels from all rows
--------------------------
My Intuition is to get a clean text file with label and text stored separately so that further modelling can be done on it.
SOLUTION
membership
This solution is only available to members.
To access this solution, you must be a member of Experts Exchange.
SOLUTION
membership
This solution is only available to members.
To access this solution, you must be a member of Experts Exchange.
ASKER
Hi,
Perfect. Many Thanks. I have the output like this.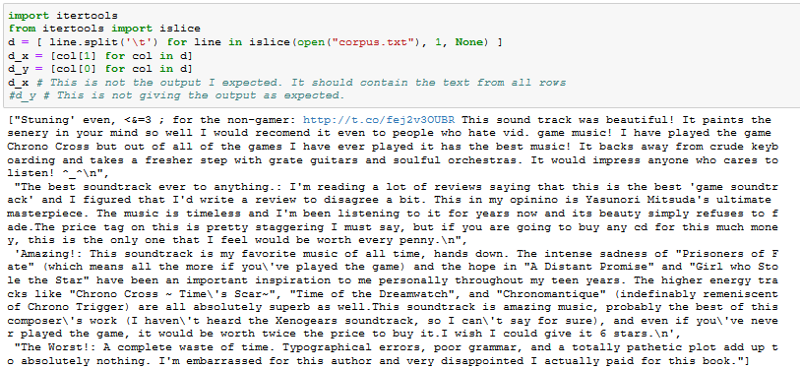
Now, I have an array of lines. In these lines, I want to do some cleaning like removing punctuation first without splitting line because I want to maintain the corresponding label and text for each row. I need to get rid of unnecessary data like apostrophe, punctuation, https, semi colon, !
I am trying with this
import re
re_punc = re.compile('[%s]' % re.escape(string.punctuati
d_x = [re_punc.sub('', w) for w in d_x]
This code successfully removes punctuation without splitting any line.
Perfect. Many Thanks. I have the output like this.
Now, I have an array of lines. In these lines, I want to do some cleaning like removing punctuation first without splitting line because I want to maintain the corresponding label and text for each row. I need to get rid of unnecessary data like apostrophe, punctuation, https, semi colon, !
I am trying with this
import re
re_punc = re.compile('[%s]' % re.escape(string.punctuati
d_x = [re_punc.sub('', w) for w in d_x]
This code successfully removes punctuation without splitting any line.
ASKER
Hi,
Before removing punctuation, can I remove/replace the http links in each of the lines?
Before removing punctuation, can I remove/replace the http links in each of the lines?
ASKER
Hi,
Along with this, I want to get rid of html escape sequences from each line, remove any number, and stop words from each line.
code to remove stop words:
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
stop_words = set(stopwords.words('engli
text = [w for w in text if not w in stop_words]
Along with this, I want to get rid of html escape sequences from each line, remove any number, and stop words from each line.
code to remove stop words:
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
stop_words = set(stopwords.words('engli
text = [w for w in text if not w in stop_words]
It could be the time to start using functions. This will help to structure your code:
This code is incomplete and upu have to add all the word processing.
but as a reasult you should have code that's easier to read
def clean_text(text):
""" cleans a text according to the requirements
- punctuation signs are removed
- stop words are remove
. . .
"""
# perform all the cleanup, that works on an entire string
text = [re_punc.sub('', text)
# text = do other stuff
# now split the text into words (if necessary),
# perform all the word based cleanup and combine all words back to one string
words = text.split()
stopwords = # please complete this line
words = [ word for word in words if word not in stopwords]
# now combine the words back to a string
text = ' '.join(words)
return text
d = [line.split('\t') for line in islice(open("corpus.txt"),
d = [cols for cols in d if len(cols) >= 2]
texts = [clean_text(cols[1]) for cols in d]
labels = [cols[0] for cols in d]
This code is incomplete and upu have to add all the word processing.
but as a reasult you should have code that's easier to read
def clean_text(text):
""" cleans a text according to the requirements
- punctuation signs are removed
- stop words are remove
. . .
"""
# perform all the cleanup, that works on an entire string
text = [re_punc.sub('', text)
# text = do other stuff
# now split the text into words (if necessary),
# perform all the word based cleanup and combine all words back to one string
words = text.split()
stopwords = # please complete this line
words = [ word for word in words if word not in stopwords]
# now combine the words back to a string
text = ' '.join(words)
return text
d = [line.split('\t') for line in islice(open("corpus.txt"),
d = [cols for cols in d if len(cols) >= 2]
texts = [clean_text(cols[1]) for cols in d]
labels = [cols[0] for cols in d]
ASKER
Hi,
It is important to replace/remove http links first before doing any pre-processing because code for removing punctuation sonverts https into simple text which has no meaning.
It is important to replace/remove http links first before doing any pre-processing because code for removing punctuation sonverts https into simple text which has no meaning.
well then just do this first in the clean_text() function
ASKER
Hi,
I tried with this code.
import re
import html
from html import parser
p = parser.HTMLParser()
uni_escape = re.compile(r'\\u[0-9a-f]{4
url_rex = re.compile(r'(http|ftp|htt
def clean_text(text):
# first replace http. it probably removes any ascii present. it does not remove ! , <=3 , & , @
unesc_html_line = html.unescape(line)
encoded_line = bytes(unesc_html_line, 'ascii', errors='ignore')
decoded_ascii_line = encoded_line.decode('ascii
unesc_line = re.sub(uni_escape, '', decoded_ascii_line)
text = url_rex.sub('', unesc_line)
# now remove punctuation
re_punc = re.compile('[%s]' % re.escape(string.punctuati
text = [re_punc.sub('', w) for w in text]
# now remove stopwords
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
stop_words = set(stopwords.words('engli
text = [w for w in text if not w in stop_words]
d = [line.split('\t') for line in islice(open("corpus.txt"),
d = [cols for cols in d if len(cols) >= 2]
d_x = [clean_text(col[1]) for col in d]
d_y = [col[0] for col in d]
d_x
I am attaching the output of the above code.
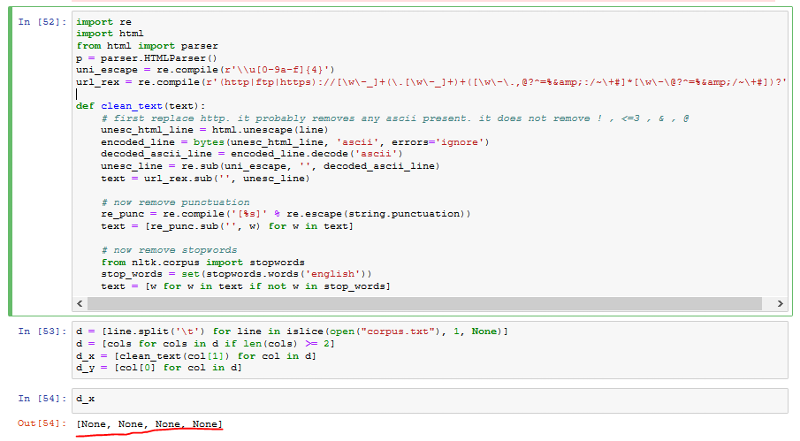
I tried with this code.
import re
import html
from html import parser
p = parser.HTMLParser()
uni_escape = re.compile(r'\\u[0-9a-f]{4
url_rex = re.compile(r'(http|ftp|htt
def clean_text(text):
# first replace http. it probably removes any ascii present. it does not remove ! , <=3 , & , @
unesc_html_line = html.unescape(line)
encoded_line = bytes(unesc_html_line, 'ascii', errors='ignore')
decoded_ascii_line = encoded_line.decode('ascii
unesc_line = re.sub(uni_escape, '', decoded_ascii_line)
text = url_rex.sub('', unesc_line)
# now remove punctuation
re_punc = re.compile('[%s]' % re.escape(string.punctuati
text = [re_punc.sub('', w) for w in text]
# now remove stopwords
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
stop_words = set(stopwords.words('engli
text = [w for w in text if not w in stop_words]
d = [line.split('\t') for line in islice(open("corpus.txt"),
d = [cols for cols in d if len(cols) >= 2]
d_x = [clean_text(col[1]) for col in d]
d_y = [col[0] for col in d]
d_x
I am attaching the output of the above code.

SOLUTION
membership
This solution is only available to members.
To access this solution, you must be a member of Experts Exchange.
SOLUTION
membership
This solution is only available to members.
To access this solution, you must be a member of Experts Exchange.
ASKER
Hi,
Concerning the last comment, I intentionally didn't use it. Though, you seem to be right but I am actually confused whether I should include the code for splitting and rejoining because I am thinking I might loose the label for that row.
I mean suppose we have 2 rows like this:
label text
1 some text
2 another more added text
if I split, I will have like this ['some','text','another','
I am not able to get my head around this. So, kindly advice.
Regards,
Concerning the last comment, I intentionally didn't use it. Though, you seem to be right but I am actually confused whether I should include the code for splitting and rejoining because I am thinking I might loose the label for that row.
I mean suppose we have 2 rows like this:
label text
1 some text
2 another more added text
if I split, I will have like this ['some','text','another','
I am not able to get my head around this. So, kindly advice.
Regards,
ASKER CERTIFIED SOLUTION
membership
This solution is only available to members.
To access this solution, you must be a member of Experts Exchange.
OK good. I hope this is what you wanted to achieve.
SOLUTION
membership
This solution is only available to members.
To access this solution, you must be a member of Experts Exchange.
ASKER
Hi,
Thanks a million. That's very good explanation and I appreciate you a lot giving your precious time explaining.
Everything seems good except can I get rid of numbers 0-9 like
<=3 is changed to 3, can i also completely remove any number present? Also, I think words like I, he, she, this (pronouns) won't do any good as well. Can I get rid of that as well.
Regards,
Thanks a million. That's very good explanation and I appreciate you a lot giving your precious time explaining.
Everything seems good except can I get rid of numbers 0-9 like
<=3 is changed to 3, can i also completely remove any number present? Also, I think words like I, he, she, this (pronouns) won't do any good as well. Can I get rid of that as well.
Regards,
ASKER
Hi,
I added more to the code. In this, I am trying to incorporate removing numbers, slang lookup, standardizing words, Split Attached Words, stemming
Might be it needs little modification to get rid of errors.
Output: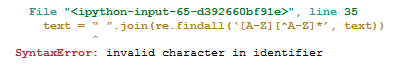
I added more to the code. In this, I am trying to incorporate removing numbers, slang lookup, standardizing words, Split Attached Words, stemming
Might be it needs little modification to get rid of errors.
import re
import string
import html
from itertools import islice
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
#from html import parser
#p = parser.HTMLParser()
uni_escape = re.compile(r'\\u[0-9a-f]{4}')
url_rex = re.compile(r'(http|ftp|https)://[\w\-_]+(\.[\w\-_]+)+([\w\-\.,@?^=%&:/~\+#]*[\w\-\@?^=%&/~\+#])?')
re_punc = re.compile('[%s]' % re.escape(string.punctuation))
def clean_text(text):
# first replace http. it probably removes any ascii present. it does not remove ! , <=3 , & , @
unesc_html_text = html.unescape(text)
encoded_text = bytes(unesc_html_text, 'ascii', errors='ignore')
decoded_ascii_text = encoded_text.decode('ascii')
unesc_text = re.sub(uni_escape, '', decoded_ascii_text)
text = url_rex.sub('', unesc_text)
#removing numbers
text = [text for word in text if text.isalpha()]
# slang lookup
text = _slang_loopup(text)
#standardizing words
text = ''.join(''.join(text) for _, text in itertools.groupby(text))
# Split Attached Words
text = “ ”.join(re.findall(‘[A-Z][^A-Z]*’, text))
# now remove punctuation
text = re_punc.sub('', text)
# split text into words
words = text.split()
# now remove stopwords
stop_words = set(stopwords.words('english'))
words = [w for w in words if not w in stop_words]
# stemming
from nltk.stem.porter import PorterStemmer
porter = PorterStemmer()
text = [porter.stem(word) for word in text]
# join words back to one word string
text = ' '.join(words)
return text
d = [line.split('\t') for line in islice(open("corpus.txt"), 1, None)]
d = [cols for cols in d if len(cols) >= 2]
d_x = [clean_text(col[1]) for col in d]
d_y = [col[0] for col in d]
print(d_x)Output:

ASKER
Thanks a ton to the expert for this answer.
Two things, that I notice:
First thing is really annoying and this can happen occasionally when copying code snippets from certain web pages.
Look very carefully at kine 35:
You seem that the quote characters are different. the leading " is different from the tailing ", Same for the single quotes.
This is great for text / literature and documents, but not many programming languages will accept these kind of special quote characters (I nfact I don't know any language accepting these, but who knows . . . )
You have to replace them with the default double quote " and the default single quote '
Then you rpython code should compile.
However I think at a first glance, that it will not do what you want. So perhaps just comment it for the moment.
The second thing you have to be very careful about:
There are two sections in your clean_text function.
One is handling the entire text string and modifying it.
In this section you have to handle the entire text, so your code will look something like
text = do_someting_with(text)
and the other section where you work with words ( the result of text.split() )
(At the end of this section you will combine the words again)
In the words section your code should look like
words = do_something_with(words)
Line 50 wants to operate on words so you should not write:
but
text = [porter.stem(word) for word in text] would get a really strange result, but line 54 ( text = ' '.join(words) ) would just overwrite this strange result.
First thing is really annoying and this can happen occasionally when copying code snippets from certain web pages.
Look very carefully at kine 35:
You seem that the quote characters are different. the leading " is different from the tailing ", Same for the single quotes.
This is great for text / literature and documents, but not many programming languages will accept these kind of special quote characters (I nfact I don't know any language accepting these, but who knows . . . )
You have to replace them with the default double quote " and the default single quote '
Then you rpython code should compile.
However I think at a first glance, that it will not do what you want. So perhaps just comment it for the moment.
The second thing you have to be very careful about:
There are two sections in your clean_text function.
One is handling the entire text string and modifying it.
In this section you have to handle the entire text, so your code will look something like
text = do_someting_with(text)
and the other section where you work with words ( the result of text.split() )
(At the end of this section you will combine the words again)
In the words section your code should look like
words = do_something_with(words)
Line 50 wants to operate on words so you should not write:
text = [porter.stem(word) for word in text]but
words = [porter.stem(word) for word in words]text = [porter.stem(word) for word in text] would get a really strange result, but line 54 ( text = ' '.join(words) ) would just overwrite this strange result.
ASKER
I am trying like this:
# load the dataset
data = open('corpus.txt').read()
labels, texts = [], []
for i, line in enumerate(data.split("\t")
content = line.split()
labels.append(content[0])
texts.append(content[1])
# create a dataframe using texts and lables
import pandas
trainDF = pandas.DataFrame()
trainDF['text'] = texts
trainDF['label'] = labels
trainDF['text']
Error is : IndexError: list index out of range
error.png