Visual Basic Classic
--
Questions
--
Followers
Top Experts
Take note that the routine GetExcelObjectFromHwnd includes the "strPtr" function. When converted from VB6 to VB.Net, .Net sends me the error message that "strPtr" is not supported. Doing further research on this problem, I find this helpful message: "Many of the Windows API calls that were necessary in Visual Basic 6.0 are now encapsulated in the .NET Framework; pointer references are no longer necessary." I would be overjoyed to find out this is the case. The functionality I'm seeking is akin to both the "Windows Task Manager" and the Windows Task Bar, shown in most Windows machines as a vertical or horizontal stripe that shows the icons of all the running applications. If I had this visibility, I could quickly isolate all the running applications of a particular type, be it Excel, Access, or anything else that is currently open. And I have little doubt the code would be both a percent or two in size of what's written below AND more robust.
Knowing the tremendous overhaul that Microsoft put into the .Net engine, I would like to get entirely out of the business of using API and hidden calls, and this is a prime spot for their banishment.
Sincerely, ~ Peter Ferber
Private Type UUID 'GUID
Data1 As Long
Data2 As Integer
Data3 As Integer
Data4(7) As Byte
End Type
Private Declare Function FindWindowEx Lib "User32" Alias "FindWindowExA" ( _
ByVal hWnd1 As Long, ByVal hWnd2 As Long, ByVal lpsz1 As String, ByVal lpsz2 As String) As Long
Private Declare Function GetClassName Lib "User32" Alias "GetClassNameA" ( _
ByVal hWnd As Long, ByVal lpClassName As String, ByVal nMaxCount As Long) As Long
Private Declare Function IIDFromString Lib "ole32" (ByVal lpsz As Long, ByRef lpiid As UUID) As Long
Private Declare Function AccessibleObjectFromWindow Lib "oleacc" ( _
ByVal hWnd As Long, ByVal dwId As Long, ByRef riid As UUID, ByRef ppvObject As Object) As Long
Function RetrieveExcelApps() As Excel.Application()
Dim TestApp As Excel.Application
Dim ReturnApps() As Excel.Application
Dim iCount As Integer
On Error GoTo MyErrorHandler
Dim hWndMain As Long
hWndMain = FindWindowEx(0&, 0&, "XLMAIN", vbNullString)
iCount = -1
If (hWndMain <> 0) Then
Do While (hWndMain <> 0)
Set TestApp = GetWbkWindows(hWndMain)
If (Not TestApp Is Nothing) Then
iCount = iCount + 1
ReDim Preserve ReturnApps(iCount)
Set ReturnApps(iCount) = GetWbkWindows(hWndMain)
End If
hWndMain = FindWindowEx(0&, hWndMain, "XLMAIN", vbNullString)
Loop
End If
RetrieveExcelApps = ReturnApps
Func_Exit:
Exit Function
MyErrorHandler:
Select Case Err.Number
Case Else:
Call MyUniversal_V2Class.PrintError(Err, "RetrieveExcelApps")
Resume Func_Exit
Resume
End Select
End Function
Private Function GetWbkWindows(ByVal hWndMain As Long) As Excel.Application
On Error GoTo MyErrorHandler
Dim hWndDesk As Long
hWndDesk = FindWindowEx(hWndMain, 0&, "XLDESK", vbNullString)
Set GetWbkWindows = Nothing
If hWndDesk <> 0 Then
Dim hWnd As Long
hWnd = FindWindowEx(hWndDesk, 0, vbNullString, vbNullString)
Dim strText As String
Dim lngRet As Long
Do While hWnd <> 0
strText = String$(100, Chr$(0))
lngRet = GetClassName(hWnd, strText, 100)
If Left$(strText, lngRet) = "EXCEL7" Then
Set GetWbkWindows = GetExcelObjectFromHwnd(hWnd)
Exit Function
End If
hWnd = FindWindowEx(hWndDesk, hWnd, vbNullString, vbNullString)
Loop
On Error Resume Next
End If
Exit Function
MyErrorHandler:
MsgBox "GetWbkWindows" & vbCrLf & vbCrLf & "Err = " & Err.Number & vbCrLf & "Description: " & Err.Description
End Function
Public Function GetExcelObjectFromHwnd(ByVal hWnd As Long) As Excel.Application
On Error GoTo MyErrorHandler
Dim fOk As Boolean
fOk = False
Dim iid As UUID
Call IIDFromString(StrPtr(IID_IDispatch), iid)
Dim obj As Object
If AccessibleObjectFromWindow(hWnd, OBJID_NATIVEOM, iid, obj) = 0 Then 'S_OK
Set GetExcelObjectFromHwnd = obj.Application
fOk = True
End If
'GetExcelObjectFromHwnd = fOk
Func_Exit:
Exit Function
MyErrorHandler:
Select Case Err.Number
Case Else:
Call MyUniversal_V2Class.PrintError(Err, "GetExcelObjectFromHwnd")
Resume Func_Exit
Resume
End Select
End FunctionZero AI Policy
We believe in human intelligence. Our moderation policy strictly prohibits the use of LLM content in our Q&A threads.
I believe that Process.GetProcesses is where you'll find all the running apps.
I found the project converter you mentioned was only good for showing what a VB.NET version of that code would look like. Learn how to do what you want using .NET and you will not regret it.
Good luck!
Running this code snippet yields an array of Processes objects that show all open Excel files.
' Get all processes running on the local computer.
Dim localAll As Process() = Process.GetProcesses()
' Get all instances of Excel running on the local computer.
' This will return an empty array if notepad isn't running.
Dim localByName As Process() = Process.GetProcessesByName("Excel")This gives me a Windows handle to the Excel files that are open, but the key question is how to translate, without using API, the System.Diagnostic.Process into an Excel Application object. The gnarlier, Dark Side-ier parts of the API-laden code, which I've demonstrated above, performs this magic. To reach home plate, I want to do that using the .Net infrastructure, and not API calls.
Thanks, ~Peter
What version of Visual Studio are you using? I have 2008, 2010, and 2012.
Using Visual Studio 2010, I added a couple of "Import" lines, getting this down to 1 error. In the property TopMostInstance, I see the error "'Hwnd' is not a member of 'Excel_Applications.Excel.
I am not familiar with the syntax of "Return (from [Application] in Me...", and I'm even having trouble finding that syntax documented. The code is clearly following the syntax of a SQL statement, with a "Where", "Order By" and "Select" clause. Would be interested to hear a little more about this routine and its function.
Seriously, I can't thank you enough. This is a great leap forward, and it demonstrates the effective use of creating wrappers, leaving the consumer with only user-friendly functionality. Solving for the one outstanding error, I will commence to testing the code functionality.
And a bonus question: can you tell me what changes I would need to make to return all the open MS ACCESS applications?
Sincerely, ~ Peter Ferber
Option Strict Off
Imports Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel
Imports System.Runtime.InteropServices
Imports System.Text
Imports Microsoft.Office.Interop
'' Based on code by JamesFaix - http://www.codeproject.com/Tips/1080611/Get-a-Collection-of-All-Running-Excel-Instances
Class ExcelApplications
Inherits List(Of Excel.Application)
Private ReadOnly rrid As New Guid("{00020400-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}")
Private Const MarshalName As String = "Excel.Application"
Private Const ProcessName As String = "EXCEL"
Private Const ComClassName As String = "EXCEL7"
Private Const DW_OBJECTID As UInt32 = &HFFFFFFF0UI
Private Const GW_HWNDPREV As UInt32 = 3
Public Sub New()
MyBase.New()
FillList()
End Sub
Public Sub New(capacity As Integer)
MyBase.New(capacity)
FillList()
End Sub
Public Sub New(collection As IEnumerable(Of Excel.Application))
MyBase.New(collection)
FillList()
End Sub
Public Sub FillList()
AddRange(From [process] In GetProcesses()
Let application = FromProcess([process])
Where application IsNot Nothing AndAlso Not Contains(application)
Select application)
End Sub
Private Function FromProcess([process] As Process) As Excel.Application
FromProcess = Nothing
Try
If [process] IsNot Nothing Then
Return InnerFromProcess([process])
End If
Catch ex As Exception
Return Nothing
End Try
End Function
Public ReadOnly Property PrimaryInstance() As Excel.Application
Get
Try
Return CType(Marshal.GetActiveObject(MarshalName), Excel.Application)
Catch ex As Exception
Return Nothing
End Try
End Get
End Property
Public ReadOnly Property TopMostInstance() As Excel.Application
Get
Try
'Hwnd' is not Aggregate member of 'Excel_Aplications.Excel.Application'."
Return (From [application] In Me
Let ZAxis = GetWindowZ([application].Hwnd)
Where ZAxis > 0
Order By ZAxis
Select [application]).FirstOrDefault()
Catch ex As Exception
Return Nothing
End Try
End Get
End Property
Public Function GetProcesses() As IEnumerable(Of Process)
Return Process.GetProcessesByName(ProcessName)
End Function
Private Function InnerFromProcess([process] As Process) As Excel.Application
Return InnerFromHandle(ChildHandleFromMainHandle([process].MainWindowHandle))
End Function
Private Function ChildHandleFromMainHandle(handle As IntPtr) As IntPtr
Dim childHandle As IntPtr = 0
EnumChildWindows(handle, AddressOf EnumChildFunction, childHandle)
Return childHandle
End Function
Private Function InnerFromHandle(handle As IntPtr) As Excel.Application
'"Type 'Excel.Window' is not defined.": changed to "Microsoft.Vbe.Interop.Window"
Dim window As Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Window = Nothing
Dim result = AccessibleObjectFromWindow(handle, DW_OBJECTID, rrid, window)
Return window.Application
End Function
Private Function GetWindowZ(handle As IntPtr) As Integer
Dim z = 0
Dim h As IntPtr = handle
While h <> IntPtr.Zero
z += 1
h = GetWindow(h, GW_HWNDPREV)
End While
Return z
End Function
Private Shared Function EnumChildFunction(hwndChild As Int32, ByRef lParam As Int32) As Boolean
Dim buffer = New StringBuilder(128)
GetClassName(hwndChild, buffer, 128)
If buffer.ToString() = ComClassName Then
lParam = hwndChild
Return False
End If
Return True
End Function
<DllImport("oleacc.dll")> _
Private Shared Function AccessibleObjectFromWindow(hwnd As IntPtr, id As UInteger, iid As Guid, <MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.IUnknown)> ByRef ppvObject As Object) As Integer
End Function
<DllImport("User32.dll")> _
Private Shared Function EnumChildWindows(hWndParent As Int32, lpEnumFunc As EnumChildCallback, ByRef lParam As Int32) As [Boolean]
End Function
<DllImport("user32.dll", CharSet:=CharSet.Auto)> _
Private Shared Function GetClassName(hWnd As IntPtr, lpClassName As StringBuilder, nMaxCount As Integer) As Integer
End Function
<DllImport("User32.dll")> _
Private Shared Function GetWindow(hWnd As IntPtr, uCmd As UInt32) As IntPtr
End Function
Private Delegate Function EnumChildCallback(hwnd As Int32, ByRef lParam As Int32) As [Boolean]
End Class





EARN REWARDS FOR ASKING, ANSWERING, AND MORE.
Earn free swag for participating on the platform.
I reference the Microsoft Office 15.0 Object Libraries (Excel 2013), and I don't have the Office 14 libraries available. I'm assuming this is not a problem.
I copied and pasted the code form1.vb and ran into a snag. I get the error "PInvokeStackImbalance was detected." in the InnerFromHandle function. In your original, you defined "window" as "Excel.Window". I actually revisited the code and made mine "Microsoft.Office.Interop.
I've included a screenshot. Any suggestions?
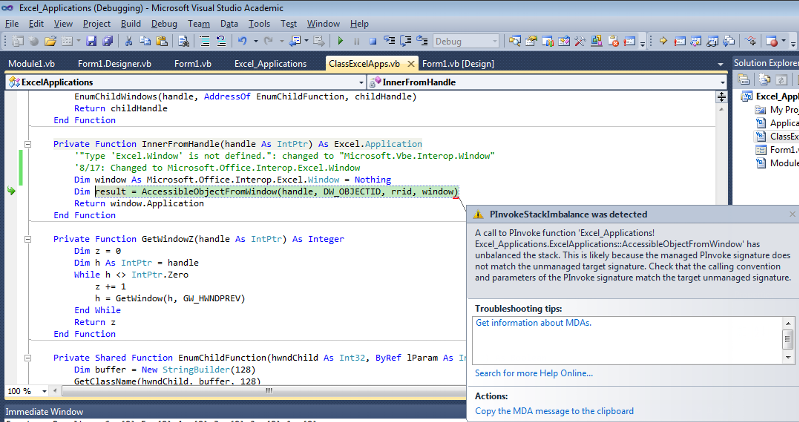
Would it be easy to list whatever modifications are necessary to produce all the open Access applications? If so, perhaps you could add that nugget. If the code would be dramatically different, I can ask it as a separate question. You're call.
Visual Basic Classic
--
Questions
--
Followers
Top Experts
Visual Basic is Microsoft’s event-driven programming language and integrated development environment (IDE) for its Component Object Model (COM) programming model. It is relatively easy to learn and use because of its graphical development features and BASIC heritage. It has been replaced with VB.NET, and is very similar to VBA (Visual Basic for Applications), the programming language for the Microsoft Office product line.