Browse All Articles > AWS Regions, Availability Zones and Edge Locations explained
AWS has developed and created its highly available global infrastructure allowing users to deploy and manage their estates all across the world through the use of the following geographical components
When architecting and designing your infrastructure it’s important to know where your data is being stored and where your instances and services are located. This is fundamental when designing and implementing a highly available and scalable network with low latency that abides by any data laws that may be in operation.
If you are studying for the AWS certifications it’s important to know the differences between Regions/Availability Zones and Edge Locations.
A Region is essentially just that, a geographic location that Amazon has selected to run and operate its Cloud services from. There are currently 12 different regions exist spanning across the globe at key locations:
North American Regions
AWS have spread these regions globally to help reduce latency for customers worldwide when accessing their resources. Within each of these regions there are a minimum of 2 Availability Zones, however typically 3 or more are usually found.
Availability zones are effectively different Data Centres located within a Region. Each AZ (Availability Zone) is completely independent of others which enable them to reside in different areas within the same Region providing a level of Business Continuity in the event of a disaster. All AZ’s within the same region are linked by extremely low latency connections allowing for the built in high availability features from many of AWS services such as S3, RDS etc to communicate with each other.
Utilising multiple AZ’s when architecting your network is essential when designing a highly available network. Deploying infrastructure across more than one allows you to ensure your service remains operational should an AZ service go down unexpectedly.
The below shows a logical diagram of the EU Ireland Region which has 3 different AZ’s (eu-west-1a, eu-west-1b and eu-west-1c) all connected by multiple low latency links
![AZlinks.png]()
Edge locations are used in conjunction with the AWS CloudFront service which is a global Content Delivery Network service (more information on CloudFront can be found here). Edge Locations are deployed across the world in multiple locations to reduce latency for traffic served over CloudFront and as a result are usually located in highly populated areas.
The below Edge Locations currently exist (as of July 2015)
North America:
Ashburn, VA (3), Atlanta, GA, Dallas/Fort Worth, TX (2), Hayward, CA, Jacksonville, FL, Los Angeles, CA (2), Miami, FL, New York, NY (3), Newark, NJ, Palo Alto, CA, San Jose, CA, Seattle, WA, South Bend, IN, St. Louis, MO
South America:
Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, São Paulo, Brazil
EMEA:
Amsterdam, The Netherlands (2), Dublin, Ireland, Frankfurt, Germany (3), London, England (3), Madrid, Spain, Marseille, France, Milan, Italy, Paris, France (2), Stockholm, Sweden, and Warsaw, Poland
Asia Pacific:
Chennai, India, Hong Kong, China (2), Manila, the Philippines, Melbourne, Australia, Mumbai, India, Osaka, Japan, Seoul, Korea (2), Singapore (2), Sydney, Australia, Taipei, Taiwan, Tokyo, Japan (2)
As you can see from below, many of the Edge Locations are located some distance away from some of the Regions discussed earlier. Edge Locations are independent of Regions and Availability Zones.
![homepage-global-infrastructure-map.png]() Image courtesy of http://aws.amazon.com/secu
Image courtesy of http://aws.amazon.com/security/sharing-the-security-responsibility/
The simple answer is ‘no’, not all services are currently available in all regions. However AWS are constantly releasing new updates and increasing the availability of their services across the globe so this is constantly evolving. The best way to find out if the service you require exists in the region you want to deploy your infrastructure is to check the AWS Regional Product Services site.
From within the AWS Console you can select the region you want to deploy your Service in. Once you have logged into the Console and are presented with the AWS dashboard, select the service you require, such as EC2.
![EC2.png]() From within the dashboard of the EC2 service you can change the Region in the top right corner by clicking on the currently select Region:
From within the dashboard of the EC2 service you can change the Region in the top right corner by clicking on the currently select Region:
![Region-Select.png]() A dropdown list with then appear allowing you to select the most appropriate Region for your needs
A dropdown list with then appear allowing you to select the most appropriate Region for your needs
![Region-Dropdown.png]()
When selecting your Region it’s generally best practise to host your infrastructure as close to the end users as possible to reduce latency.
Once you have selected the Region for your Service you wish to deploy your infrastructure in you can then deploy your EC2 instances. During your deployment of your EC2 instances at the Configure Instance Details screen you will be prompted to select an Availability Zone that resides within that Region.
![Select-AZ.png]() Architecting your applications and services across multiple Availability Zones and multiple Regions provides is best practise when designing a highly available infrastructure network. Should any natural or other disaster at a particular AZ or Region you will be safe in the knowledge that your customers will not be affected due to your careful design.
Architecting your applications and services across multiple Availability Zones and multiple Regions provides is best practise when designing a highly available infrastructure network. Should any natural or other disaster at a particular AZ or Region you will be safe in the knowledge that your customers will not be affected due to your careful design.
By default many of the AWS services and functions operate across multiple AZs by design for these very same reasons, such as S3, RDS Multi AZ, ELB, AutoScaling to name but a few.
Thank you for taking the time to read my article, if you have any feedback please do leave a comment below.
If you liked this article or found it helpful please click the 'Good Article' button at the bottom of this article, it would be very much appreciated.
I look forward to your comments and suggestions.
Stuart Scott - (LinkedIn)
![AWS-Logo.jpg]() -AWS Certified Solutions Architect
-AWS Certified Solutions Architect
-AWS Accredited Technical Professional
-AWS Accredited Business Professional
-AWS Accredited TCO and Cloud Economics
- Regions
- Availability Zones
- Edge Locations
When architecting and designing your infrastructure it’s important to know where your data is being stored and where your instances and services are located. This is fundamental when designing and implementing a highly available and scalable network with low latency that abides by any data laws that may be in operation.
If you are studying for the AWS certifications it’s important to know the differences between Regions/Availability Zones and Edge Locations.
What is an AWS Region?
A Region is essentially just that, a geographic location that Amazon has selected to run and operate its Cloud services from. There are currently 12 different regions exist spanning across the globe at key locations:
North American Regions
- US East (Northern Virginia)
- US West (Northern California)
- US West (Oregon)
- AWS GovCloud (US) – Reserved for Government agencies only
- São Paulo
- EU (Ireland)
- EU (Frankfurt)
- Asia Pacific (Singapore)
- Asia Pacific (Tokyo)
- Asia Pacific (Sydney)
- Asia Pacific (Seoul)
- China (Beijing) – Limited Public release
AWS have spread these regions globally to help reduce latency for customers worldwide when accessing their resources. Within each of these regions there are a minimum of 2 Availability Zones, however typically 3 or more are usually found.
What is an Availability Zone?
Availability zones are effectively different Data Centres located within a Region. Each AZ (Availability Zone) is completely independent of others which enable them to reside in different areas within the same Region providing a level of Business Continuity in the event of a disaster. All AZ’s within the same region are linked by extremely low latency connections allowing for the built in high availability features from many of AWS services such as S3, RDS etc to communicate with each other.
Utilising multiple AZ’s when architecting your network is essential when designing a highly available network. Deploying infrastructure across more than one allows you to ensure your service remains operational should an AZ service go down unexpectedly.
The below shows a logical diagram of the EU Ireland Region which has 3 different AZ’s (eu-west-1a, eu-west-1b and eu-west-1c) all connected by multiple low latency links
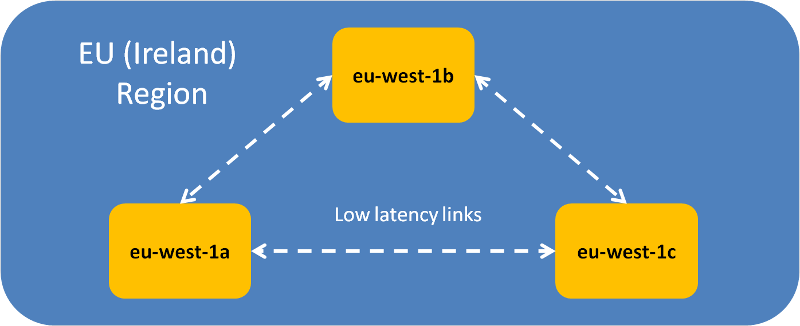
What is an Edge Location
Edge locations are used in conjunction with the AWS CloudFront service which is a global Content Delivery Network service (more information on CloudFront can be found here). Edge Locations are deployed across the world in multiple locations to reduce latency for traffic served over CloudFront and as a result are usually located in highly populated areas.
The below Edge Locations currently exist (as of July 2015)
North America:
Ashburn, VA (3), Atlanta, GA, Dallas/Fort Worth, TX (2), Hayward, CA, Jacksonville, FL, Los Angeles, CA (2), Miami, FL, New York, NY (3), Newark, NJ, Palo Alto, CA, San Jose, CA, Seattle, WA, South Bend, IN, St. Louis, MO
South America:
Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, São Paulo, Brazil
EMEA:
Amsterdam, The Netherlands (2), Dublin, Ireland, Frankfurt, Germany (3), London, England (3), Madrid, Spain, Marseille, France, Milan, Italy, Paris, France (2), Stockholm, Sweden, and Warsaw, Poland
Asia Pacific:
Chennai, India, Hong Kong, China (2), Manila, the Philippines, Melbourne, Australia, Mumbai, India, Osaka, Japan, Seoul, Korea (2), Singapore (2), Sydney, Australia, Taipei, Taiwan, Tokyo, Japan (2)
As you can see from below, many of the Edge Locations are located some distance away from some of the Regions discussed earlier. Edge Locations are independent of Regions and Availability Zones.
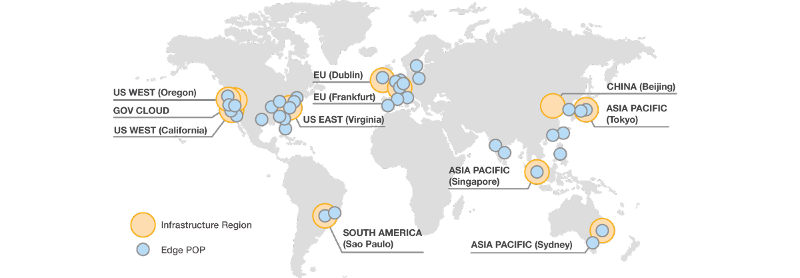 Image courtesy of http://aws.amazon.com/secu
Image courtesy of http://aws.amazon.com/secuCan I get any Service in any Region?
The simple answer is ‘no’, not all services are currently available in all regions. However AWS are constantly releasing new updates and increasing the availability of their services across the globe so this is constantly evolving. The best way to find out if the service you require exists in the region you want to deploy your infrastructure is to check the AWS Regional Product Services site.
Selecting a Region for a resource within the AWS Console
From within the AWS Console you can select the region you want to deploy your Service in. Once you have logged into the Console and are presented with the AWS dashboard, select the service you require, such as EC2.
 From within the dashboard of the EC2 service you can change the Region in the top right corner by clicking on the currently select Region:
From within the dashboard of the EC2 service you can change the Region in the top right corner by clicking on the currently select Region:
 A dropdown list with then appear allowing you to select the most appropriate Region for your needs
A dropdown list with then appear allowing you to select the most appropriate Region for your needs
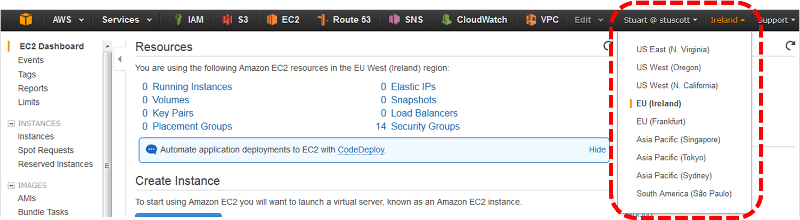
When selecting your Region it’s generally best practise to host your infrastructure as close to the end users as possible to reduce latency.
Once you have selected the Region for your Service you wish to deploy your infrastructure in you can then deploy your EC2 instances. During your deployment of your EC2 instances at the Configure Instance Details screen you will be prompted to select an Availability Zone that resides within that Region.
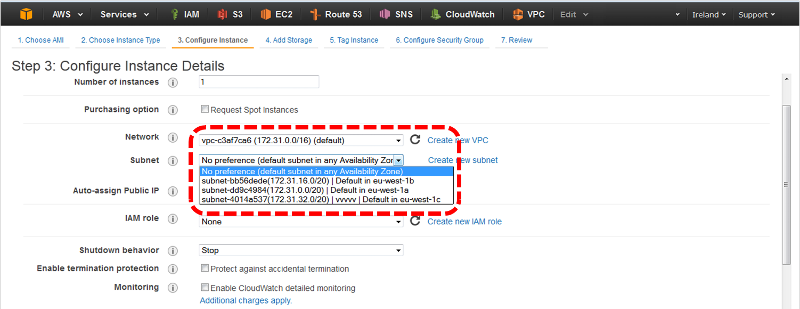 Architecting your applications and services across multiple Availability Zones and multiple Regions provides is best practise when designing a highly available infrastructure network. Should any natural or other disaster at a particular AZ or Region you will be safe in the knowledge that your customers will not be affected due to your careful design.
Architecting your applications and services across multiple Availability Zones and multiple Regions provides is best practise when designing a highly available infrastructure network. Should any natural or other disaster at a particular AZ or Region you will be safe in the knowledge that your customers will not be affected due to your careful design.
By default many of the AWS services and functions operate across multiple AZs by design for these very same reasons, such as S3, RDS Multi AZ, ELB, AutoScaling to name but a few.
Thank you for taking the time to read my article, if you have any feedback please do leave a comment below.
If you liked this article or found it helpful please click the 'Good Article' button at the bottom of this article, it would be very much appreciated.
I look forward to your comments and suggestions.
Stuart Scott - (LinkedIn)
 -AWS Certified Solutions Architect
-AWS Certified Solutions Architect-AWS Accredited Technical Professional
-AWS Accredited Business Professional
-AWS Accredited TCO and Cloud Economics
Have a question about something in this article? You can receive help directly from the article author. Sign up for a free trial to get started.


Comments (2)
Commented:
You have mentioned here as " many of the Edge Locations are located some distance away from some of the Regions " i cant get this point.have doubt like whether locations will come under region?
Justnow i have started to learn about cloud.
Thanks by,
Prathap
Author
Commented:Thank you for your comment.
Edge location are different from Regions, and as a result do not fall under 'Regions' as a location. To put the global infrastructure in it's most simple form the different elements can be described as follows:
- Availability Zones (AZs): These are essentially the physical data centers of AWS. This is where the actual compute, storage, network, and database resources are hosted
- Regions: A Region is a collection of availability zones that are geographically located close to one other. This is generally indicated by AZs within the same city. Regions do not include Edge Locations, only AZs
- Edge Locations: These are AWS sites deployed in major cities and highly populated areas across the globe and they far outnumber the number of availability zones available. These are used to reduce latency to end users by using the AWS CDN service known as CloudFront. You are unable to deploy your typical compute, storage, and database services in Edge Locations, the Edge Locations are reserved for simply reducing latency using CloudFront and Lambda@Edge services.
I hope this helps.
Cheers,
Stu...